EXIF Data: Understanding, Finding, Using, and Removing It
Key Takeaways:
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format Data) is essential metadata stored in an image file, detailing aspects like shutter speed, aperture, ISO, white balance, camera model, flash mode, and more. This data provides useful information about the settings used to take a particular photo.
Understanding and using EXIF data can help improve photography skills, particularly regarding photo sharpness, light balance, and noise control. Examining the shutter speed, aperture, and ISO settings can assist in understanding the reasons behind the quality of a photo and allow for adjustments for better results.
EXIF data can be viewed and edited on various platforms (Windows PC, Mac, and smartphone). However, the level of detail in EXIF data may vary depending on the device used. EXIF data can also be removed entirely for privacy reasons or to avoid sharing particular details about the photo or equipment used.
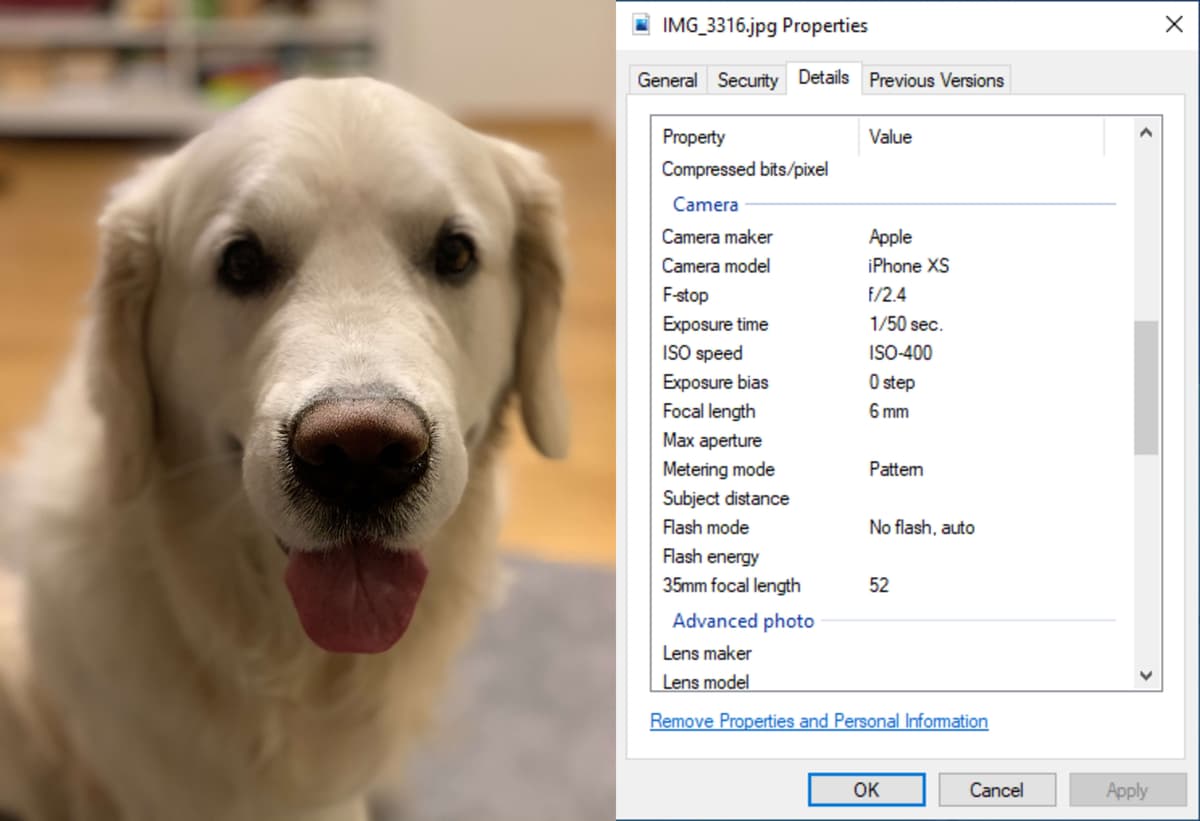
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format Data) is the data from camera settings stored in an image file. This data includes settings like shutter speed, max aperture, ISO, white balance, camera model and make, flash mode, metering mode, focal length, and more, but a lot of it is rarely ever used. In addition to photo information, metadata on equipment information, serial numbers, and copyright information is also stored in EXIF Data.
Understanding and Using EXIF Data
Two settings EXIF Data is largely used for are shutter speed and aperture. If a photo is blurry or just does not appear very sharp, this is most likely due to shutter speed. When viewing EXIF Data, a slower shutter speed is more likely to have blurred areas than a photo with a faster shutter speed, due to what is happening in front of the camera lens being quicker than the shutter speed. The sharpness of an image can be attributed to the same thing, with the shutter speed not being adjusted to the slight movements of a picture and the focused object’s edges.
Aperture can also be the cause of an image being blurry or not as sharp as one would like. A higher aperture number means the camera takes in less light, while a lower number means the camera takes in more light. This helps focus and sharpness as light from other areas in the photo can outshine the main object of the image, putting it less into the visible foreground of the photo.
Another thing to consider that EXIF Data can help with is the ISO details. If your camera’s ISO is set to auto, it will help you learn what exact ISO settings work and what do not. If the image has a lot of digital noise, it might be worth checking if the ISO setting is too high.
Viewing EXIF Data
Immediately after a picture is taken, the EXIF Data can be viewed on the camera’s monitor. Most of the time, it can be seen by scrolling through the information settings, to find the exact way to check it for your camera, check the manual for detailed information on viewing EXIF Data on your exact camera model.
On a Windows PC, there are dedicated EXIF Data viewer software programs available that specialize in viewing and editing EXIF Data, but file explorer also has this capability. In file explorer, right-click the image you wish the see the data for. A window should pop up with various options. Click Properties > Details. This will then bring up EXIF Data for the photo.
On a Mac devices, open the image with Preview. Click Tools > Show Inspector > EXIF tab.
When viewing an image taken on an phone like the example here (iPhone XS), you may notice a few things are different. For starters, a lot of fields are missing, like Max aperture, Subject distance, and Flash energy for starters. Some fields also are not as detailed as on a normal camera, like Flash mode, only telling whether the flash was on, off, or auto, rather than the true mode and further details about the type of flash the camera produced. So, while EXIF Data is not as useful with a phone, it still can help you learn a lot about the pictures taken on one, and the contrast to images taken on a camera, allowing you to learn more deeply about both.
Removing EXIF Data
Many cameras and devices will allow EXIF Data to not be recorded at all, or at least restrict what gets recorded. Once loaded to a computer, you will also have the option to remove or alter EXIF Data completely.
To remove EXIF Data on a PC, right-click the picture and click Properties > Details. At the bottom of the box, a “Remove Properties and Personal Information” option will appear. This will then give you the choice of making a copy of the photo with the information removed or remove the information from the original.
To remove EXIF Data on a Mac, open the photo using Preview, go to Tools > Show Inspector > ‘i’ tab > EXIF option, then delete the data.
FAQs:
What is EXIF data? EXIF, or Exchangeable Image File Format Data, is metadata stored within an image file. It contains information about the camera settings used when the photo was taken, such as shutter speed, aperture, ISO, white balance, camera model, flash mode, and more. This data provides detailed insights into the conditions and equipment used when capturing a particular image.
How can understanding and using EXIF data improve my photography skills? Understanding EXIF data can significantly improve your photography skills by allowing you to analyze the specific settings used in successful shots, and apply them to future work. For example, if a photo appears blurry, the EXIF data might reveal a slow shutter speed, suggesting a need for adjustment in similar shooting conditions in the future. Similarly, examining aperture settings in the EXIF data can help with controlling light and achieving the desired sharpness in your photos.
How can I view the EXIF data of a photo on a Windows PC or Mac? On a Windows PC, you can view EXIF data by right-clicking the image, selecting Properties, and then the Details tab. There are also dedicated EXIF viewer software programs available. On a Mac, you can view EXIF data by opening the image with Preview, then selecting Tools > Show Inspector > EXIF tab.
Why would the EXIF data from a smartphone be different from that of a traditional camera? Smartphones, while capable of capturing high-quality images, often have less detailed EXIF data compared to traditional cameras. Certain fields like max aperture, subject distance, and flash energy might be missing or not as detailed. However, the existing EXIF data from a smartphone can still provide valuable insights into the photo's shooting conditions and camera settings.
What are the steps to remove EXIF data from a photo? EXIF data can be removed on a PC by right-clicking the photo, clicking Properties > Details, and at the bottom of the box, selecting "Remove Properties and Personal Information". This gives you the option of making a copy of the photo with the information removed or removing the information from the original. On a Mac, you can open the photo using Preview, go to Tools > Show Inspector > 'i' tab > EXIF option, and then delete the data.
Latest Blog Posts

Reverse image search - things you should know
Dive into the intriguing world of reverse image search. This guide illuminates its mechanics, benefits, and myriad applications. Learn how it empowers digital investigation, from validating image origins to discovering visually similar content.
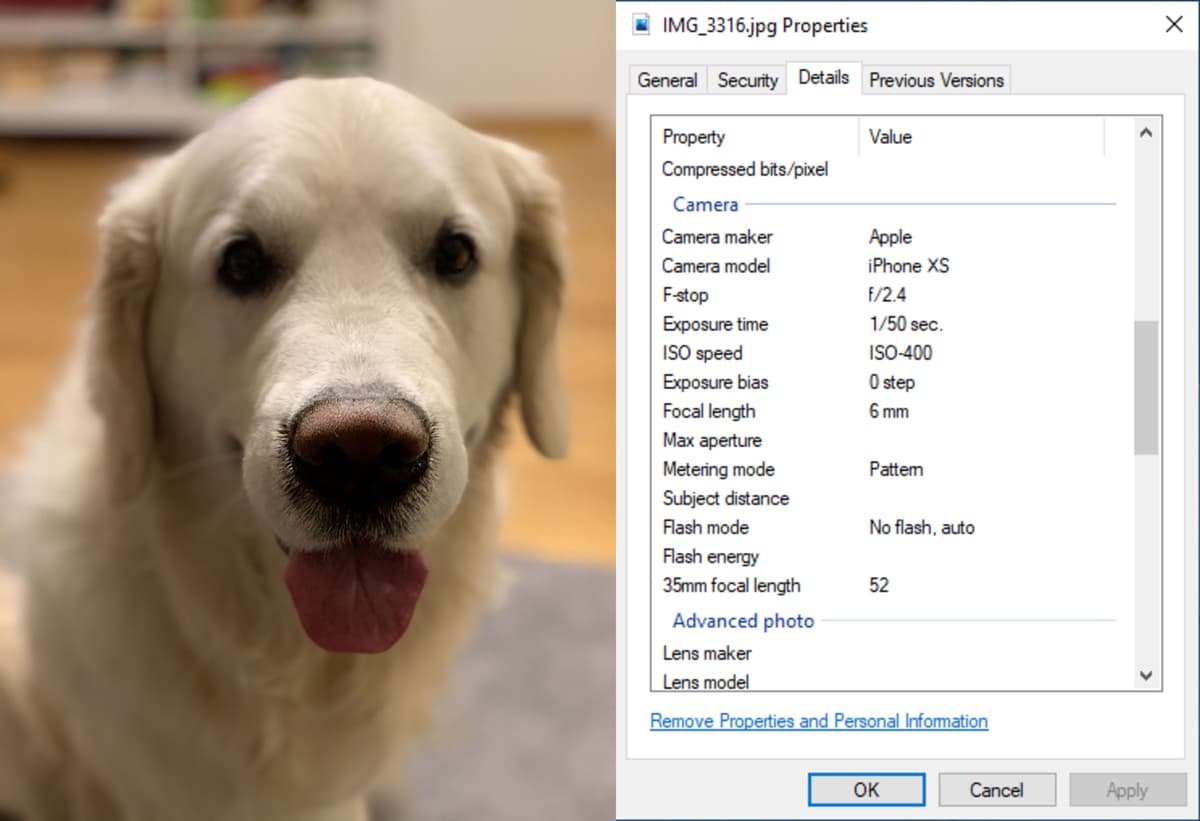
EXIF Data: Understanding, Finding, Using, and Removing It
EXIF is the data from camera settings stored in an image file. This data includes settings like shutter speed, max aperture, ISO, white balance, camera model and make, flash mode, metering mode, focal length, and more.
How to Reverse Image Search on iPhone?
Reverse image search is a valuable tool for finding the original source of an image, verifying its authenticity, or discovering similar images. This article will walk you through the process of performing a reverse image search on your iPhone.
Why Copyseeker still the best reverse image search engine?
As the landscape of reverse image search engines continues to evolve, one platform consistently outshines its competitors – Copyseeker. In 2022, it was recognized as the best, and it has only upped its game since then.